10 J There are 2 steps to solve this one. Expert-verified Share Share Step 1 To solve this question we are going to use the work energy theorem. According to the work energy the… View the full answer Step 2 Unlock Answer Unlock Previous question Next question Not the question you’re looking for? Post any question and get expert help quickly.
Physics Reference: Two blocks, A and B, are on a horizontal frictionless surface. The blocks are joined together by a spring, as shown in Fig. 2.1.
A block initially at rest on a horizontal, frictionless surface is accelerated by a constant horizontal force of 5.0 newtons. If 15 joules of work is done on the block by this force while accelerating it, the kinetic energy of the block increases by a.) 3.0 J b.) 15 J c.) 20 J d.) 75 J This problem has been solved!

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
The change in momentum of block B is: Twice the change in momentum of block A. The same as the change in momentum of block A. Half the change in momentum of block A. . F D. avg D P = t. Two identical blocks, B having twice the mass of A, are initially at rest on frictionless air tracks. You now apply the same constant force to both blocks for

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
Initially, both the blocks are at rest on horizontal surface as shown wooden block initially at rest. The surface of the table is frictionless and 70 cm above the floor level. After the collision the bullet becomes embedded into the block. The bullet-block system slides off the top of the table and strikes the floor. a. Find the momentum of the bullet before the collision. p1 = m1v1 = (0.01 kg)(500 m/s) = 5 kg m/s
Source Image: uomustansiriyah.edu.iq
Download Image
A Block Initially At Rest On A Horizontal Frictionless Surface
wooden block initially at rest. The surface of the table is frictionless and 70 cm above the floor level. After the collision the bullet becomes embedded into the block. The bullet-block system slides off the top of the table and strikes the floor. a. Find the momentum of the bullet before the collision. p1 = m1v1 = (0.01 kg)(500 m/s) = 5 kg m/s A .60kg block initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface is acted upon by a force of 4.0 N for a distance of 6.5 m. … A .60-kg block initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface is acted upon by a force of 4.0 N for a distance of 6.5 m. How much kinetic energy does the block gain? … So,initially it was at rest,and
Example. A Block Pulled on a Frictionless Surface A 6.00-kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a horizontal fr
01/02/2017 Physics High School answered • expert verified A block initially at rest on a horizontal, frictionless surface is accelerated by a constant horizontal force of 5 newtons. if 15 joules of work is done on the bock by this force, the kinetic energy of the block increases by Advertisement Expert-Verified Answer question A 1.5kg block is initially rest on a horizontal frictionless surface when a horizontal force in the positive direction of x-axis is applied to the block. The force is given by F (

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
Two blocks rest on a horizontal frictionless surface as shown in the f 01/02/2017 Physics High School answered • expert verified A block initially at rest on a horizontal, frictionless surface is accelerated by a constant horizontal force of 5 newtons. if 15 joules of work is done on the bock by this force, the kinetic energy of the block increases by Advertisement Expert-Verified Answer question
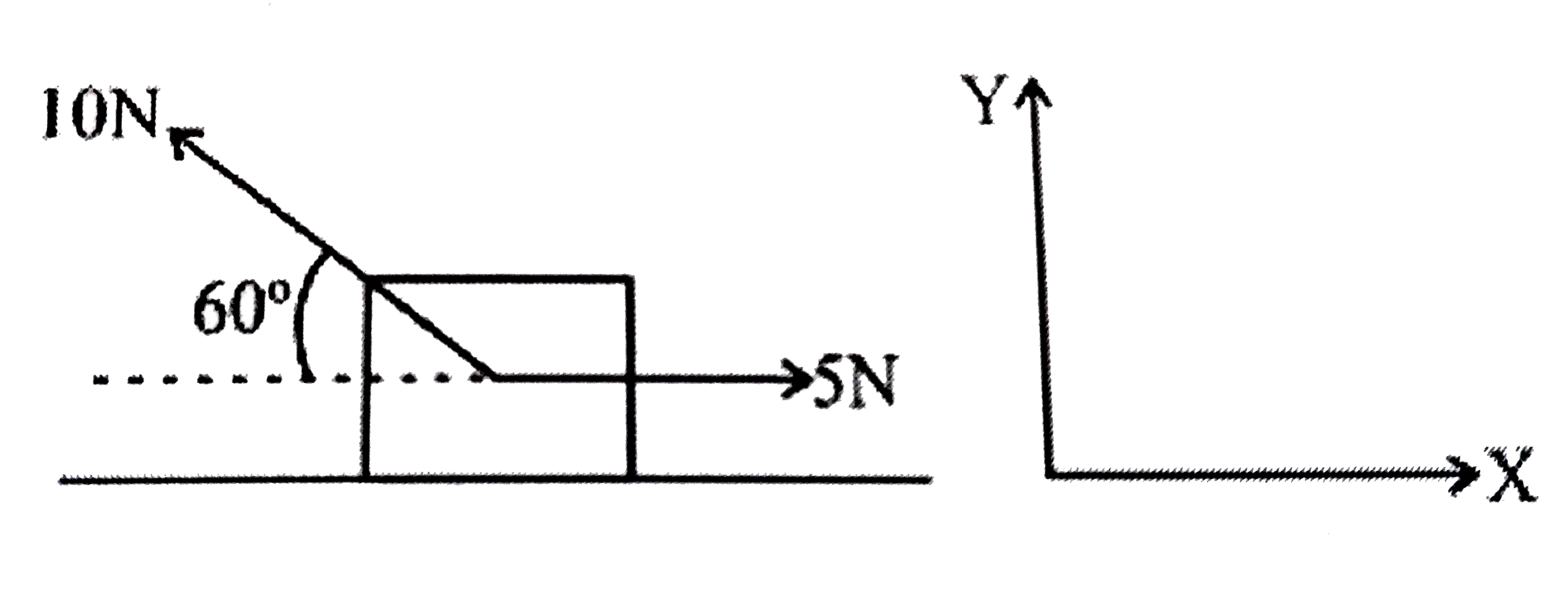
Source Image: doubtnut.com
Download Image
Physics Reference: Two blocks, A and B, are on a horizontal frictionless surface. The blocks are joined together by a spring, as shown in Fig. 2.1. 10 J There are 2 steps to solve this one. Expert-verified Share Share Step 1 To solve this question we are going to use the work energy theorem. According to the work energy the… View the full answer Step 2 Unlock Answer Unlock Previous question Next question Not the question you’re looking for? Post any question and get expert help quickly.
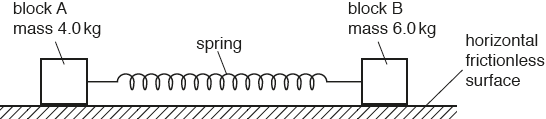
Source Image: physics-ref.blogspot.com
Download Image
Initially, both the blocks are at rest on horizontal surface as shown The change in momentum of block B is: Twice the change in momentum of block A. The same as the change in momentum of block A. Half the change in momentum of block A. . F D. avg D P = t. Two identical blocks, B having twice the mass of A, are initially at rest on frictionless air tracks. You now apply the same constant force to both blocks for
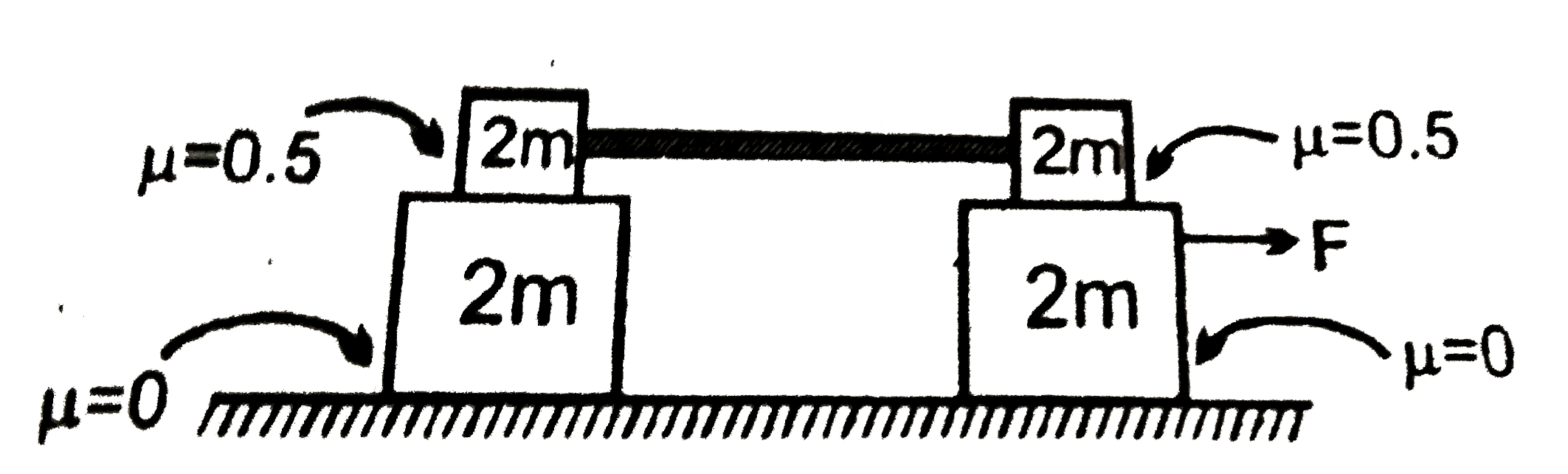
Source Image: doubtnut.com
Download Image
SOLVED: A 3 kg block rests on a horizontal, frictionless surface as shown in Figure. The block is pressed back against a spring having a constant of k = 625 N/m, compressing A `1.5 kg` block is initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface. A horizontal force `vec F=(4-x^(2))hat i` is applied on the block. Initial positi
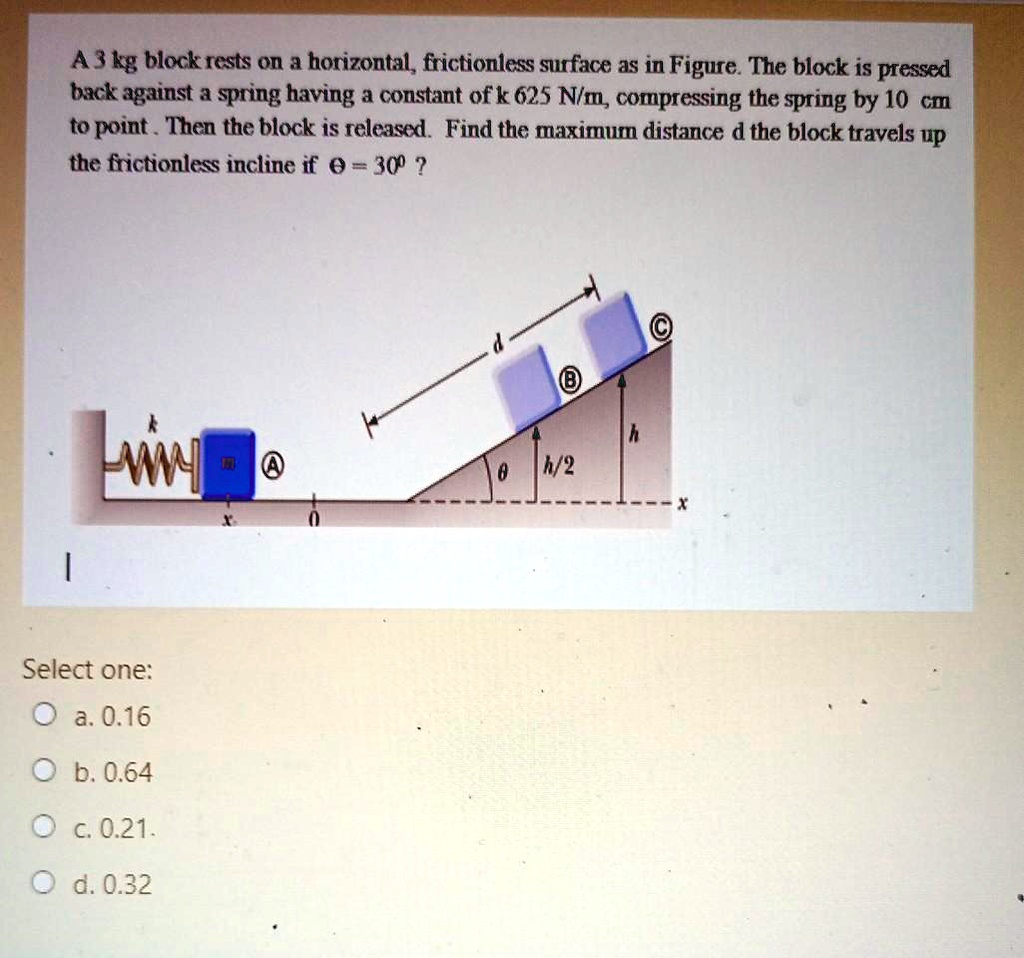
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
A block is initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface when a horizontal force – YouTube wooden block initially at rest. The surface of the table is frictionless and 70 cm above the floor level. After the collision the bullet becomes embedded into the block. The bullet-block system slides off the top of the table and strikes the floor. a. Find the momentum of the bullet before the collision. p1 = m1v1 = (0.01 kg)(500 m/s) = 5 kg m/s

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
A `1.5-kg` block is initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface when a horizontal – YouTube A .60kg block initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface is acted upon by a force of 4.0 N for a distance of 6.5 m. … A .60-kg block initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface is acted upon by a force of 4.0 N for a distance of 6.5 m. How much kinetic energy does the block gain? … So,initially it was at rest,and

Source Image: youtube.com
Download Image
Two blocks rest on a horizontal frictionless surface as shown in the f
A `1.5-kg` block is initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface when a horizontal – YouTube A block initially at rest on a horizontal, frictionless surface is accelerated by a constant horizontal force of 5.0 newtons. If 15 joules of work is done on the block by this force while accelerating it, the kinetic energy of the block increases by a.) 3.0 J b.) 15 J c.) 20 J d.) 75 J This problem has been solved!
Initially, both the blocks are at rest on horizontal surface as shown A block is initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface when a horizontal force – YouTube A `1.5 kg` block is initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface. A horizontal force `vec F=(4-x^(2))hat i` is applied on the block. Initial positi